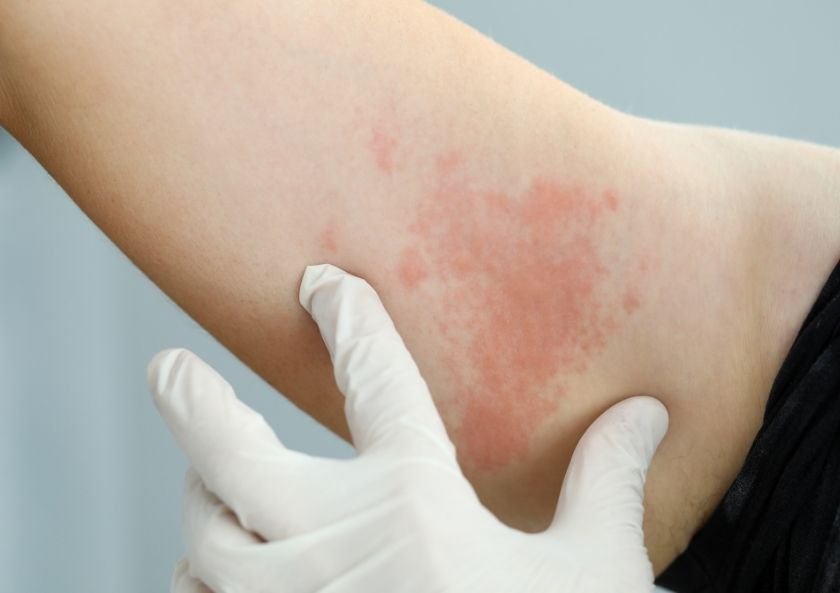
Treatment of hives (urticaria) consists of sudden itchy rashes on the skin. The size and color of the hives on the skin may vary from person to person. Since hives usually last between 24 and 48 hours, families do not prefer to wait for it to pass and go to the doctor. Correct diagnosis and treatment is important so that the itchy rash does not affect your child. So, how is the treatment of hives, we explained in this article.
Hives (Urticaria) Treatment
Treatment of hives (urticaria) may not require treatment if the symptoms of hives are not very severe in your child and do not recur. Most of the time, the hives may go away on their own. However, a treated urticaria is helpful in relieving itching, serious discomfort, and persistent symptoms.
Hives (Urticaria) Drug Treatment
We can list the drugs used for the treatment of hives as follows;
Anti-itch drugs: The standard drugs used in the treatment of hives are antihistamines. These drugs eliminate itching, swelling and other allergy symptoms.
Anti-inflammatory drugs: In very severe cases of hives, allergists may recommend oral corticosteroids. These medications help prevent blistering, redness and itching on the skin.
Drugs that affect the immune system: In cases where antihistamines and corticosteroids do not work, your doctor may prescribe drugs to calm the overactive immune system.
Medicines to prevent pain and swelling: Hives can also be treated with anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs called leukotriene antagonists.
Medicines that control blood protein: If there is a genetic condition of urticaria, such medicines reduce the symptoms by controlling the level of certain proteins in the blood and relieve your child.
Treatment for Emergencies
In very severe episodes of hives, it’s also helpful to go to an emergency room or even get an adrenaline injection.
What Happens If Hives Are Not Treated?
Since hives are usually short-lived and can go away on their own, families skip the treatment step unless it causes very serious conditions. However, long-term untreated hives can cause other unwanted health problems.
We can list the consequences that may arise when hives are not treated as follows;
Difficulty in breathing: If the swelling in the body also occurs in your child’s mouth and throat, difficulty in breathing and therefore fainting may occur. If you have swelling of the mouth, tongue, or throat, seek immediate medical attention.
Serious allergic reactions: Anaphylaxis is a severe allergic shock that affects the heart and lungs. Symptoms of anaphylaxis are narrowing of the airways and difficulty breathing. For this reason, blood pressure drops, it gives a feeling of tiredness, fainting may occur.
Diseases That May Occur in a Person with Hives (Urticaria)
- Thyroid diseases
- Lupus skin
- Joint inflammation
- Sjogren’s syndrome
- Celiac disease
- Type 1 diabetes disorders