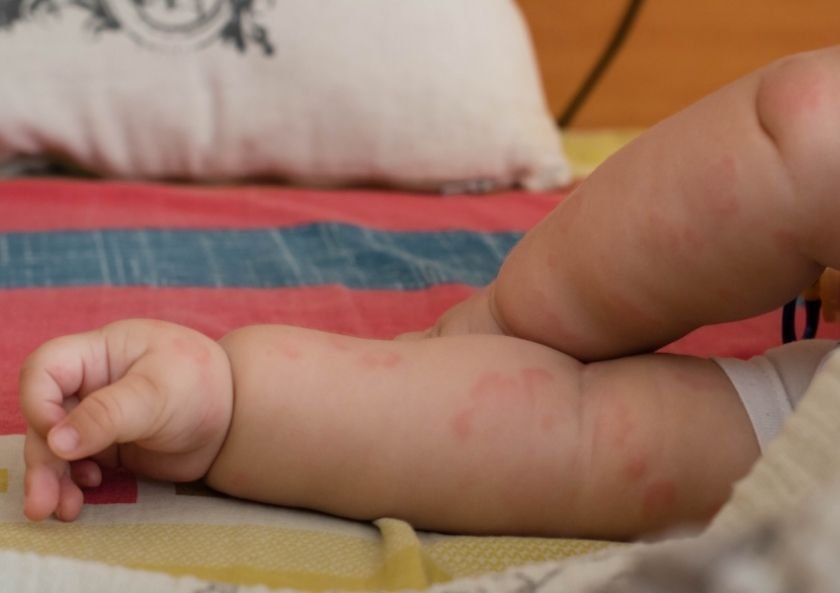
Urticaria in children, also known as hives among the people, is pale red bumps that form in groups on any part of the skin. Angioedema is a swelling like urticaria; however, the swelling is under the skin rather than the surface. Urticaria and angioedema often occur together.
What are the symptoms of Urticaria in Children?
The bumps associated with hives can be as follows:
- Red or skin color
- Intense itchy
- Roughly oval or worm-shaped
- A few centimeters or much bigger
Most hives disappear spontaneously within 24 hours, but chronic hives can recur for months or years.
What are the symptoms of angioedema?
Angioedema is a hives-like reaction that affects the deeper layers of the skin. It is most commonly seen around the eyes, cheeks or lips. Angioedema and hives can occur separately or simultaneously.
Among the signs and symptoms of angioedema
- Wide, thick, hard bulge
- Swelling and redness
- Pain or temperature is present in the affected areas.
How is urticaria (hives) diagnosed in children?
Your doctor will examine your puffiness or swelling areas if they are still present and will take a careful medical history to identify possible causes. In some cases, an allergy skin test may be recommended. If hereditary angioedema is a possible diagnosis, certain blood tests may be done to check the levels and functions of some blood proteins.
Which doctor should be visited for urticaria (hives) disease in children?
Family physicians can diagnose and recommend treatment options for urticaria. However, in more severe or chronic cases, your doctor may refer you to an allergy-immunologist. These specialists have been specially trained in diagnosis and treatment.
What are the types of urticaria in children?
Some urticaria are classified as acute urticaria, while other cases are chronic. The difference depends on how long the symptoms last.
Acute Urticaria (Hives)
The word “acute” means for a short time. Urticaria that last less than 6 weeks are called acute urticaria. Acute urticaria can occur after contact with an allergen such as food, animal dander, insect bite, latex or pollen. Identifying and preventing the trigger can help prevent this allergic reaction from recurring.
Medicines can potentially trigger urticaria. Urticaria can also occur for non-allergic reasons. These can be in the form of heat, stress, exercise or exposure to certain chemicals. One of the most common causes of acute hives in children is viral infections.
Chronic Urticaria (Hives)
Unlike acute urticaria, chronic urticaria last longer. Most people suffering from chronic urticaria have symptoms that last more than a year. In many cases, chronic urticaria is idiopathic, this means its exact cause cannot be identified. Only a small percentage of chronic urticaria is caused by an allergy.
Urticaria Treatment in Children
Often, if symptoms progress mildly, treatment may not be needed. Many hives and angioedema cases resolve on their own. However, treatment can provide relief for intense itching, serious discomfort, or ongoing symptoms.
Medication Treatment
Urticaria and angioedema treatment may include the following prescription medications:
- Anti-itch drugs. Antihistamines, which are the standard treatment for hives and angioedema, are drugs that reduce itching, swelling and other allergy symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. For severe urticaria or angioedema, doctors can sometimes suggest an oral corticosteroid to reduce redness, swelling, and itching.
- Drugs that suppress the immune system. If antihistamines and corticosteroids are not effective, doctor may prescribe a drug that is able to soothe overactive immune system.
- Medicines that reduce pain and swelling. Chronic hives and angioedema can be treated with a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug called leukotriene antagonists.
- Blood protein controllers. If hereditary angioedema is involved, levels of certain blood proteins can be regulated and various signs and symptoms can be alleviated with various medications.
Urticaria (Hives) Treatment in Pregnant Women
Small rashes may tend to disappear on their own. However, it is important not to rub the affected area. Soap can aggravate the situation, so it will be helpful to reduce the amount of soap used. An alternative method that can reduce itching is to take an oatmeal bath or use baking soda in the bath. Moisturizing the skin well can help itch and dry.
With the use of antihistamines, which are considered safe during pregnancy, relief or treatment may be provided. It is important to review any medication warnings and consult your pharmacist and healthcare provider before taking any medication.
Frequently asked questions about urticaria (hives) disease in children
If you’re looking for other treatments for your hives, a variety of natural solutions can help.
Is there any herbal treatment for urticaria?
- Oatmeal bath: A glass of unbaked oatmeal added to bath water soothes itching and relieves pain. Make sure you have a cold bath. If it is very hot, water can cause itching and swelling to continue.
- Turmeric powder: Being a member of the ginger family, this main ingredient in curry can relieve inflammation and help heal wounds. It can be used to add flavor to fish, meat, rice, vegetables and pasta. Controlled use is important. Excess consumption may cause dizziness and nausea.
- Aloe vera lotion: It is a substance rich in vitamin E, which provides healthy skin. It can also reduce itching caused by hives.
Does Urticaria (Hives) last a lifetime?
Urticaria that last more than 6 weeks are called chronic urticaria.
If the reason cannot be determined even after a detailed history and tests, it is named chronic idiopathic hives. (“Idiopathic” means that it is not due to a specific reason but occurs spontaneously.) About half of these cases are associated with some immune findings. Chronic urticaria can also be associated with thyroid disease, other hormonal problems, or, in very rare cases, cancer.
Is urticaria sexually transmitted?
Hives itself are not contagious unless viruses that cause it (if so) are transmitted from one infected person to another. Hives are more common in children and women. In general, if the affected individual is no longer exposed to the allergen, the urticaria decrease and disappear in about 24-48 hours.
Can urticaria patients take a bath?
Urticaria patients can have baths normally, but make sure the water is warm and the washing time should be limited to 10 minutes. Alternatively, it may be possible to relieve itching by adding a product containing colloidal oatmeal to bath water. It is necessary to use a gentle, odorless cleanser and avoid foaming, scented lotions. After the bath, it will be useful to dry it with a towel and rub a moisturizing cream or lotion on moist skin.
Does hives pass from mother to baby?
Hives are not contagious, except for those caused by viral infection and cannot be transmitted from mother to child. During breastfeeding, the baby can continue breastfeeding.
Does stress cause urticaria?
Everyone struggles with stress from time to time, and stress can affect more than just our emotional health. Stress might cause symptoms, such as a rash, that can increase your stress.
Factors such as a viral infection, other diseases or environmental triggers can cause hives. Stress is considered as an environmental trigger.